For healthcare professionals

Evidence of variation: excipients and pH, impacting safety
The research of Professor Miriam Kolko from Copenhagen University Hospital shows that factors like preservatives, phosphates and pH can influence tolerability.1
Preservatives (e.g benzalkonium chloride) in glaucoma eye drops:
Benzalkonium chloride (BAK) is used as a preservative in the majority of glaucoma eye drops. It is toxic to the ocular surface, causing unnecessary side effects (ocular surface changes, conjunctival inflammation, discomfort, tear film instability, subconjunctival fibrosis, epithelial apoptosis, corneal surface impairment), leading to potential risk of failure for future glaucoma surgery.13

It causes mitochondrial dysfunction14-15 and Goblet cell death16.
BAK also accumulates and damages the deeper structures in the eye, such as the trabecular meshwork13-14,17-20, potentially increasing outflow resistance and reducing the impact of IOP-lowering agents21.
Professor Kolko's recommendations are: 22
- To reduce the use of BAK-containing eye drops as there is no reason for BAK to be in glaucoma eye drops.
- To make a case for changing the patient treatment algorithm to authorities so BAK is phased out from the eye drops.
- It is time to make this change for the benefit of patients.
Find out more from the glaucoma experts:
Prof. Miriam Kolko, Professor in Translational Eye Research, University of Copenhagen:
Prof. Anthony King, Consultant Ophthalmologist, Nottingham University Hospital:
Phosphates in glaucoma eye drops:
Some of the eye drops contain phosphate buffers. In 2012 the European Medicines Agency announced that pharmaceutical companies should clearly state in the Summary of Product Characteristics if a product contains phosphates, because phosphates can cause corneal calcification leading to significant corneal damage.3
“The Summary of Product Characteristics should have the following wording added to Section 4.8 (Undesirable effects): Cases of corneal calcification have been reported very rarely in association with the use of phosphate containing eye drops in some patients with significantly damaged corneas.”3
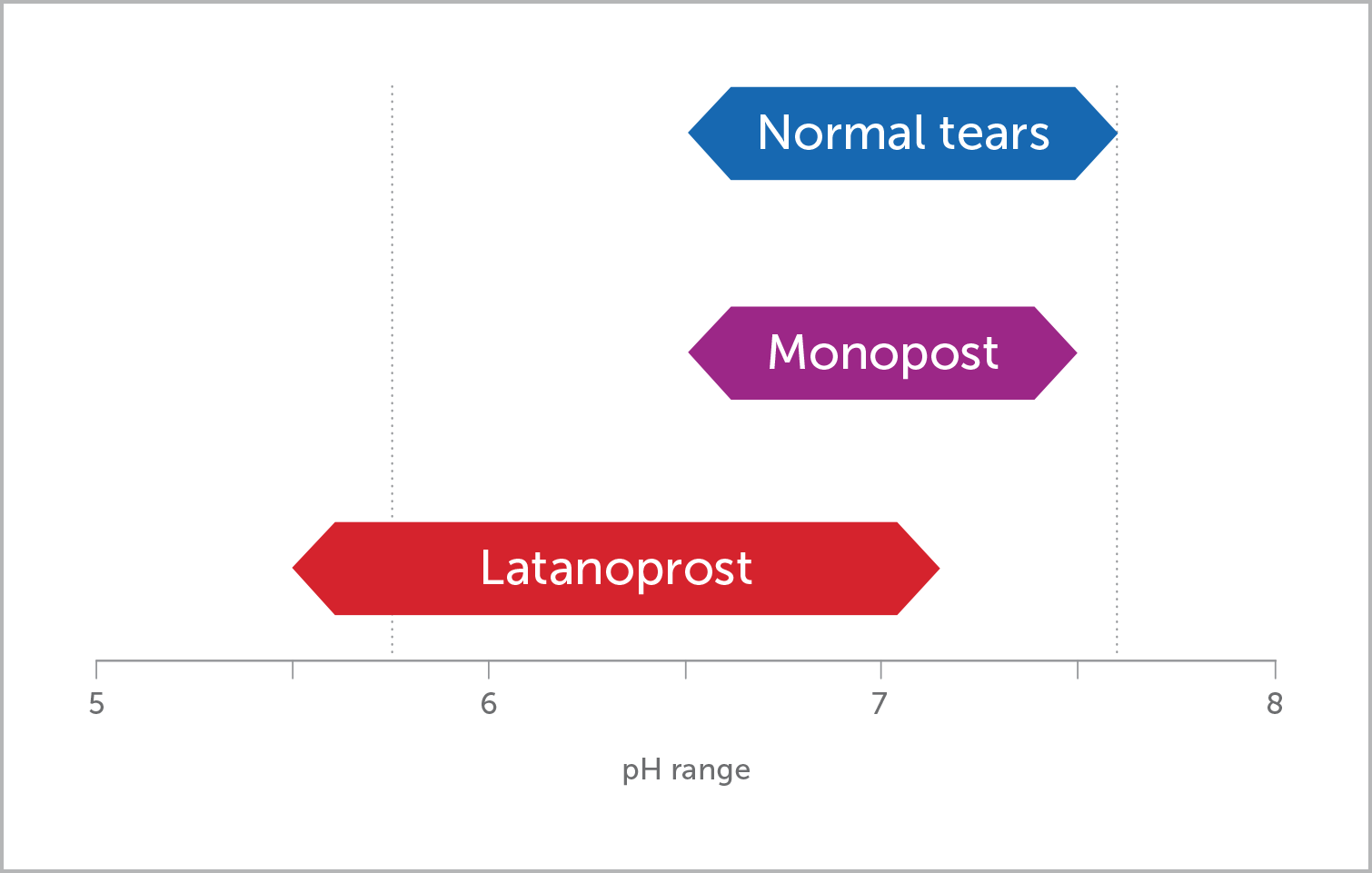
The pH value:
The physical properties of generic eyedrops may differ from the original in multiple ways, one of them being the pH value.1
If the eye drop is too acidic or too alkaline, it can cause irritation,22 tearing, ocular pain and discomfort.24
To optimise ocular comfort, the pH value of an eyedrop should match the tear film24
• pH range for `normal' tears is 6.5 to 7.6.25
• pH of latanoprost generics ranges from 5.5 to 7.2.26-27